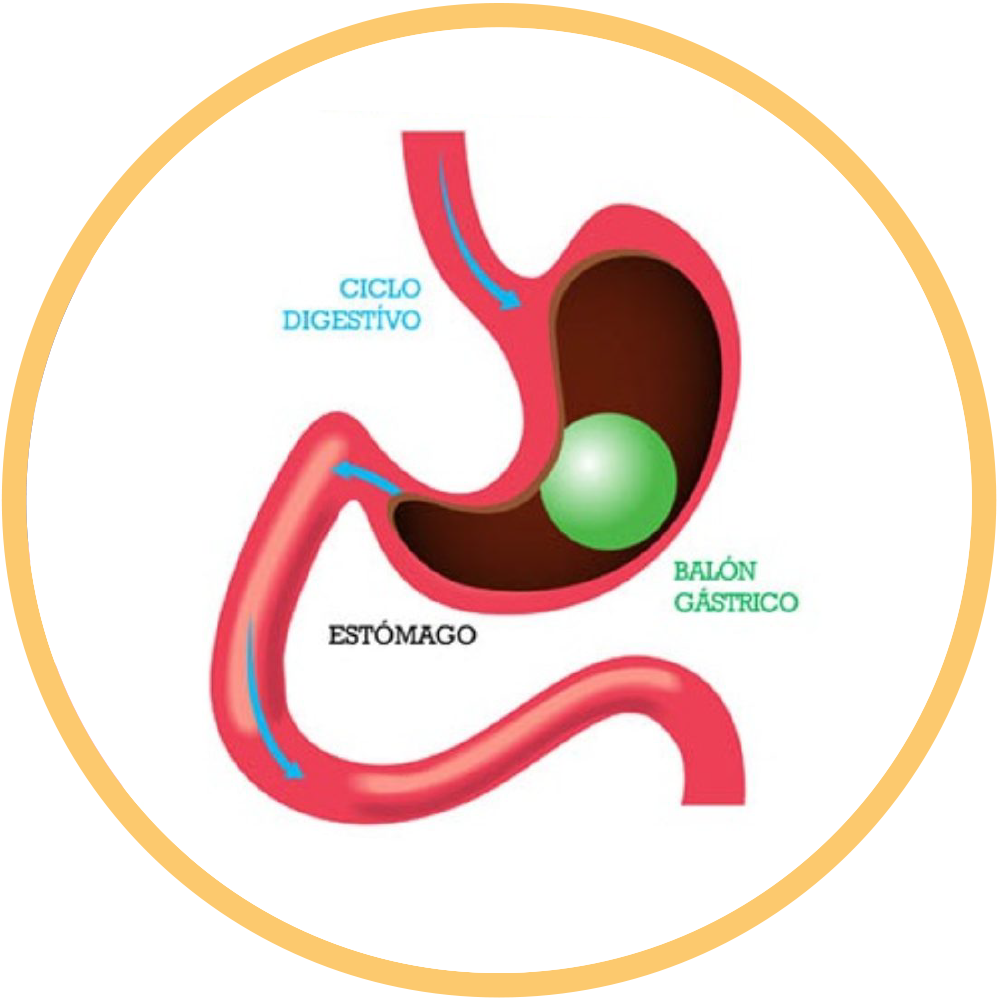
Intragastric balloon placement is a minimally invasive, non-surgical technique with a low complication rate and considerable weight loss.
It is a non-surgical alternative for patients who have not achieved the desired weight loss with diet and exercise; in addition, it is considered a bridge for those patients with contraindication for a definitive initial surgical procedure. The mechanism of balloon weight loss is restrictive, since any balloon with a volume of 400ml or more can induce satiety. Another possible mechanism of action that can also contribute to weight loss is the delay in gastric emptying that it causes.
There is controversy regarding defining a patient at high risk of developing complications in bariatric surgery. Risk factors include a BMI> 60, age over 50 years, and the presence of medical conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and deep vein thrombosis. To minimize the risk of cardiovascular and respiratory complications in this group of patients, different strategies have been designed to reduce weight safely; For this reason, non-operative strategies have been designed, such as the use of an intragastric balloon placed endoscopically as the first phase of definitive bariatric treatment. For the group of patients with low BMI (30-34) the balloon is, in many cases, the only procedure allowed to treat their obesity. The loss of excess weight varies between 11 and 15 kg after the placement of the balloon at 6 months6, which represents the average loss of excess weight of 26.5 and 25.4% at 3 and 6 months after removal of the balloon.